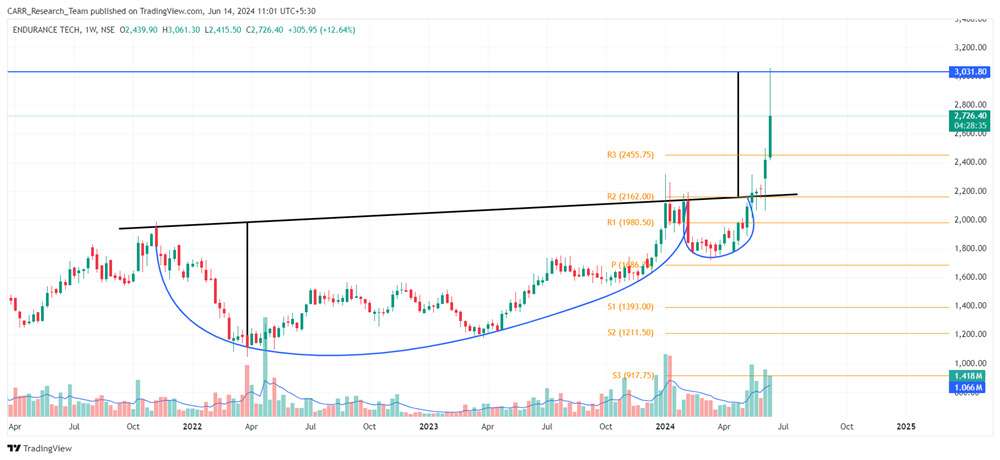
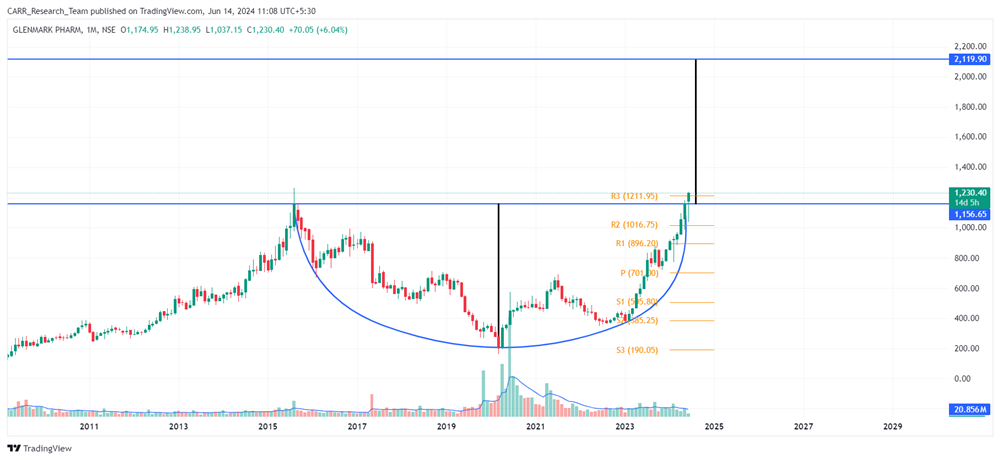
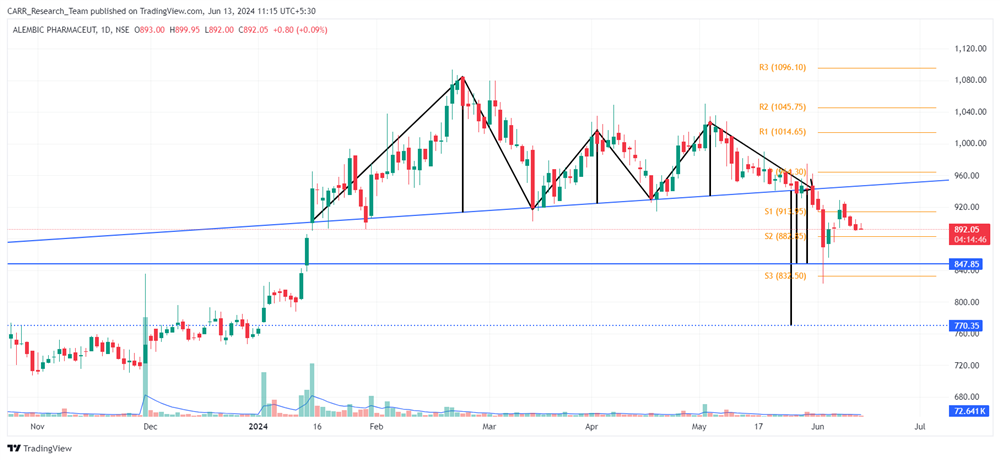
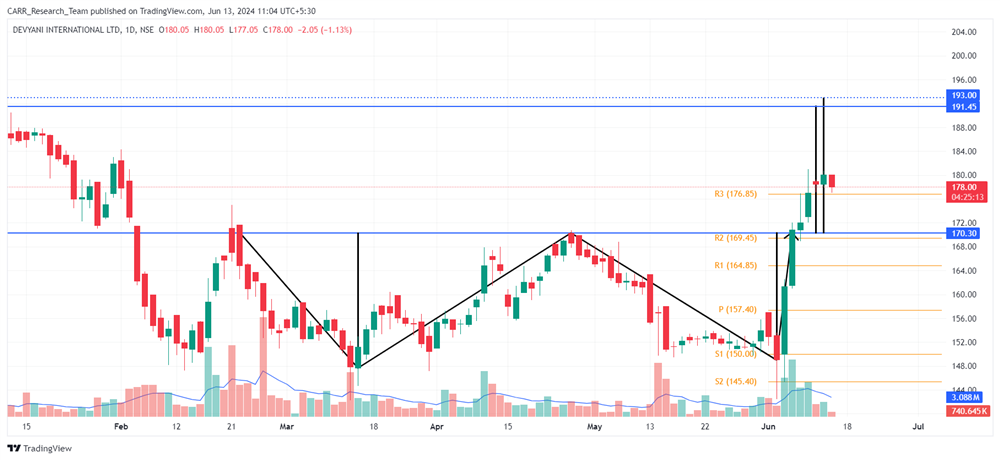
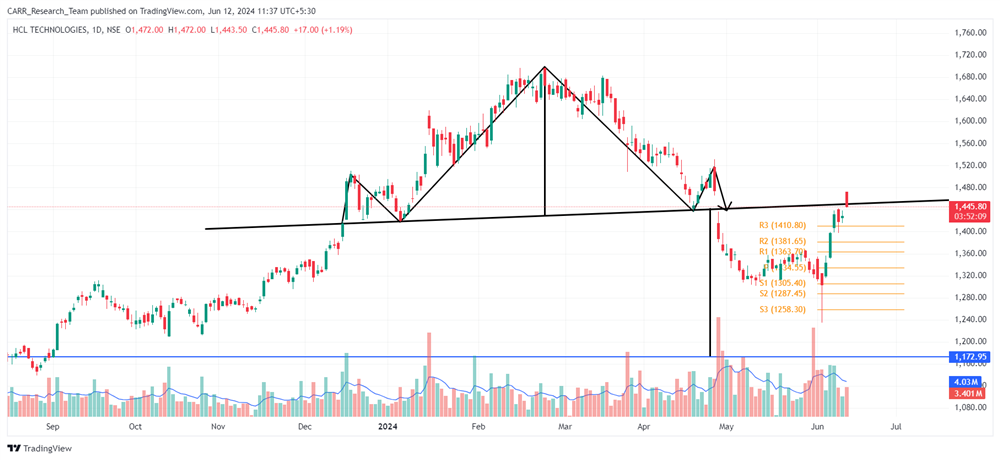
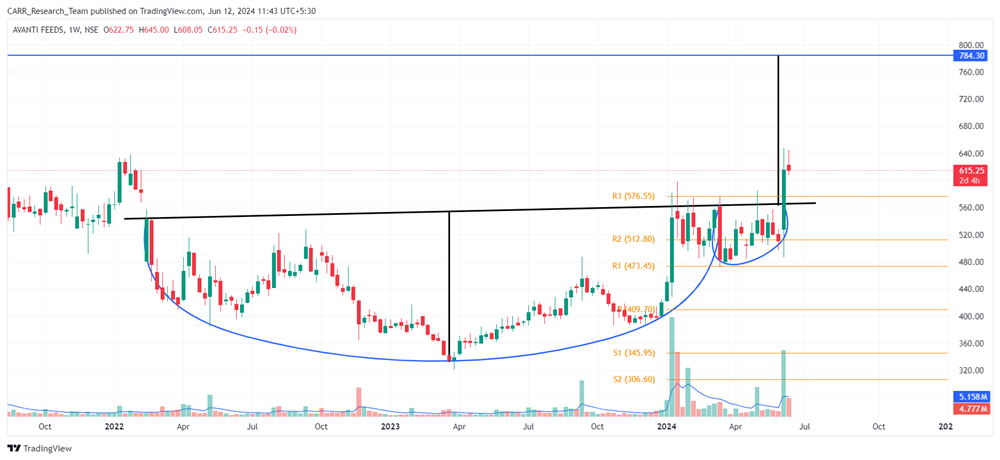
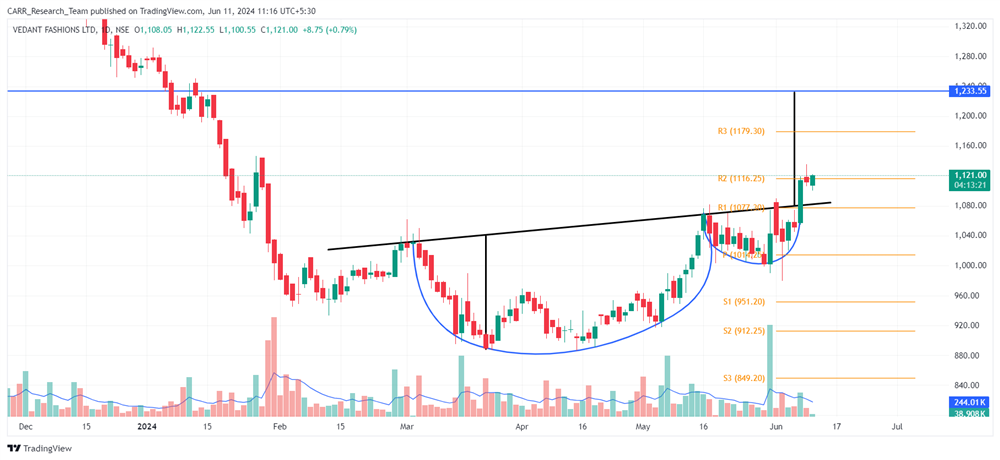
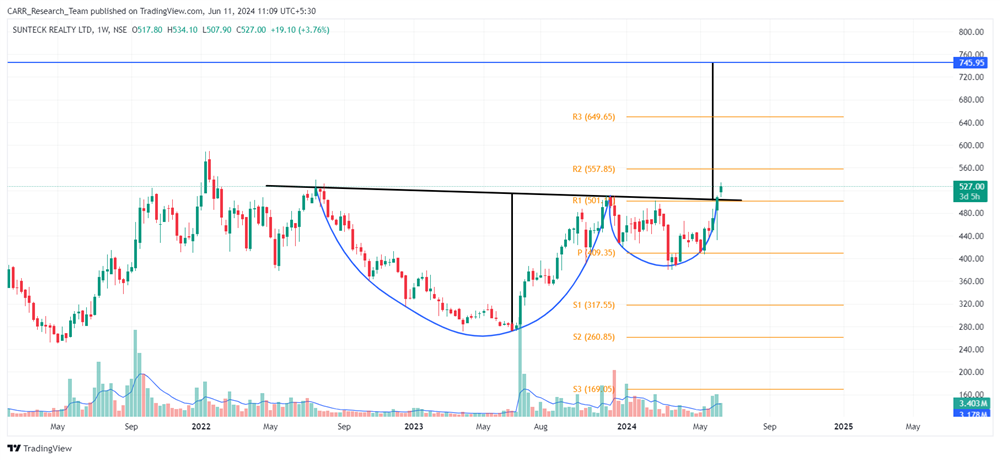
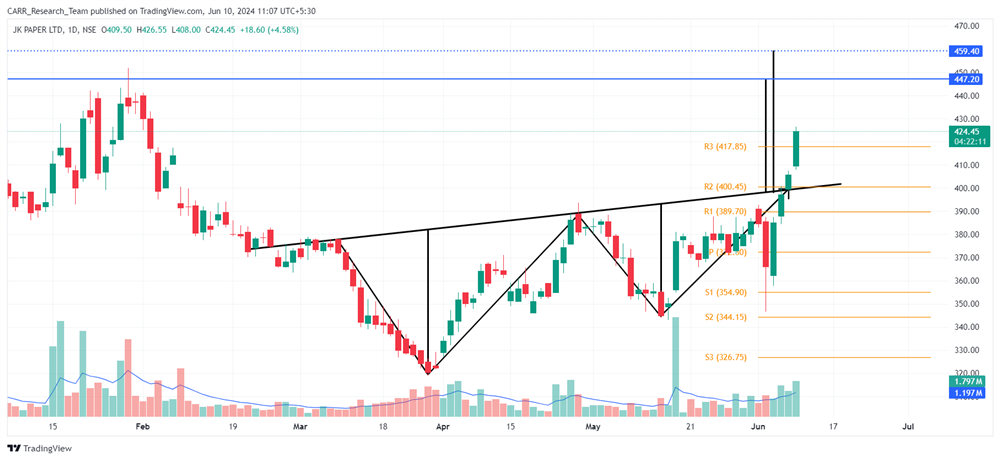
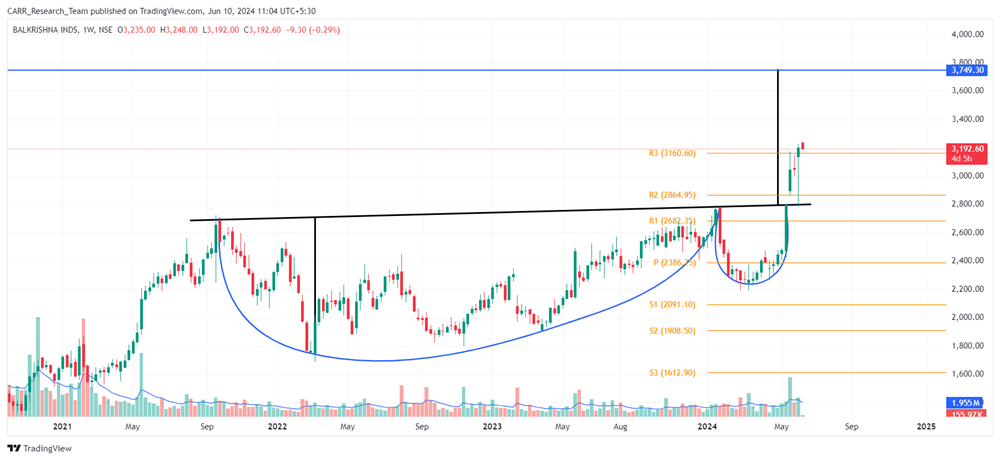
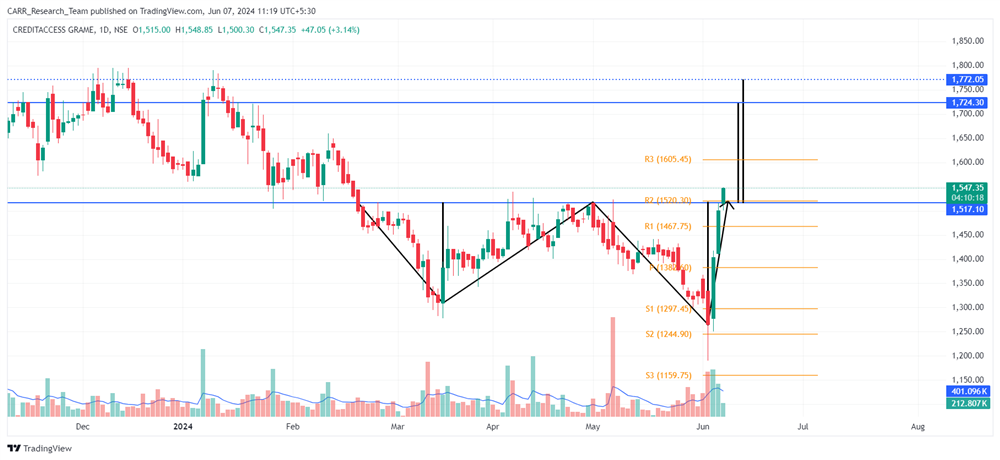
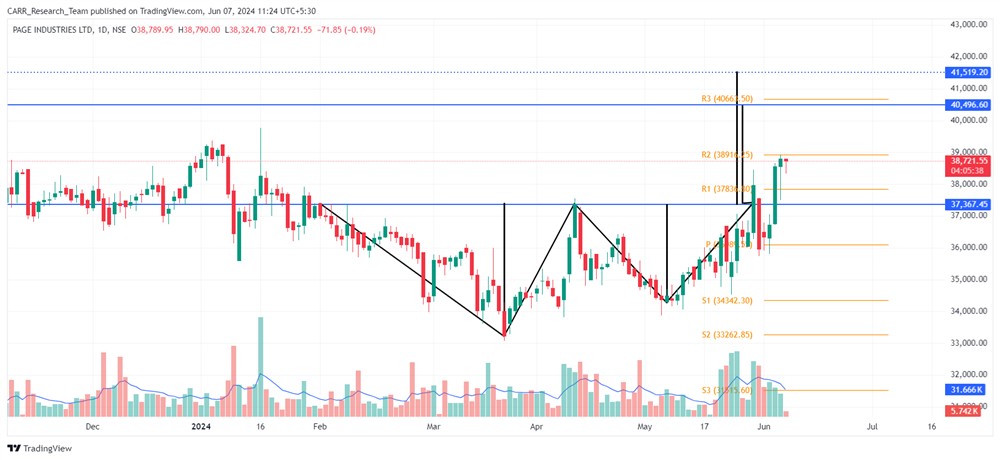
The upcoming 2024 Union Budget of India, set to be presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, is generating significant anticipation among industry leaders, economists, and the general public. Scheduled for the latter part of July 2024, this budget will be the first of the third term of the NDA government led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, commonly referred to as the Modi 3.0 government. The 2024-25 Budget is expected to outline the Modi 3.0 government's economic agenda, which likely includes initiatives to fast-track reforms aimed at transforming India into a $5-trillion economy in the near future and achieving 'Viksit Bharat' by 2047. As the nation navigates economic recovery and growth post-pandemic, this budget is anticipated to address key issues and provide a comprehensive financial roadmap for the upcoming year. Here’s an in-depth look at what to expect from the 2024 budget based on pre-budget consultations and expert opinions.
Industry Consultations and Stakeholder Engagement: In preparation for the budget, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman is scheduled to hold pre-budget meetings with industry stakeholders on June 20, 2024. Prior to this, an official meeting with the Revenue Secretary will take place on June 18. These consultations are crucial for the government to gather input from various sectors, understand their challenges, and incorporate their suggestions into the budget. Key discussion areas are likely to include tax policies, incentives for startups, infrastructure development, and measures to boost manufacturing and exports.
Economic Growth and Fiscal Consolidation: Economic growth and fiscal consolidation are expected to be central themes in the 2024 budget. With Prime Minister Modi's government entering its third term, there is an emphasis on balancing populist spending with rigorous economic reforms. The budget is likely to focus on stimulating economic growth through increased investment in infrastructure, promoting digital economy initiatives, and enhancing the ease of doing business. Concurrently, measures to control the fiscal deficit and public debt will be critical to ensuring sustainable economic health.
Tax Reforms and New Income Tax Rules: A significant expectation from the budget is the introduction of new income tax rules. There is speculation that the government might discontinue the old tax regime in favour of a simplified tax structure, although it remains to be seen if such a drastic change will be implemented immediately in the first budget of the new government. The goal would be to simplify tax compliance for individuals and businesses, broaden the tax base, and enhance revenue collection. Potential changes could include adjustments to tax slabs, incentives for savings and investments, and measures to reduce tax evasion.
Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure development is anticipated to receive substantial attention in the 2024 budget. The government is expected to allocate significant funds for the expansion of road networks, railways, and urban infrastructure. Investments in renewable energy projects and advancements in digital infrastructure, such as the 5G rollout and rural broadband connectivity, will also be prioritized. These initiatives are essential for economic growth as well as for improving connectivity and access to services across the country.
Social Welfare and Healthcare: The budget is likely to emphasize social welfare programs, particularly in healthcare and education. Enhanced funding for public health infrastructure, the availability of essential medicines, and investment in medical research are expected to be key components. Education reforms, including the integration of digital learning tools and vocational training programs, will aim to equip the workforce with relevant skills. Increased allocations for social security schemes targeting vulnerable sections of society will help ensure a robust safety net.
Environmental Sustainability: Environmental sustainability will be a significant focus of the 2024 budget. The government is expected to introduce policies aimed at combating climate change, reducing carbon emissions, and promoting green energy. Investments in solar and wind energy, initiatives to improve energy efficiency, and subsidies for environmentally friendly practices will be central to these efforts. Incentives for businesses and individuals to adopt green technologies are also anticipated.
Push in Rural Spending: There has been a noticeable pattern in consumption recovery where wealthier individuals are spending more, while rural consumption remains low, with demand for basic and affordable goods still subdued post-pandemic. This indicates that lower-income individuals, who were hit hardest by the pandemic, haven't yet regained their purchasing power. Limited financial aid for vulnerable groups and irregular weather patterns impacting rural earnings have exacerbated this gap. To address this disparity, the government is likely to boost spending in rural areas. Increased investment in rural infrastructure, agriculture, and social welfare programs will be crucial to reviving demand and ensuring balanced economic growth.
Conclusion: The 2024 Union Budget of India is poised to address critical economic and social challenges while setting the stage for sustainable growth. By focusing on economic stability, infrastructure development, tax reforms, social welfare, environmental sustainability, and boosting rural spending, the government aims to create a resilient and prosperous future for the country. In addition to these, it will be also be crucial to see how the biggest ever RBI dividend of Rs. 2.1 Lakh Crore is utilised by the government. The key question is whether the ₹2.1-lakh crore surplus should be fully used for fiscal consolidation, partly allocated to social welfare schemes given the new coalition government, or entirely invested in boosting public infrastructure. As we await the detailed announcements, it is clear that this budget will play a pivotal role in shaping India's economic trajectory in the coming years.