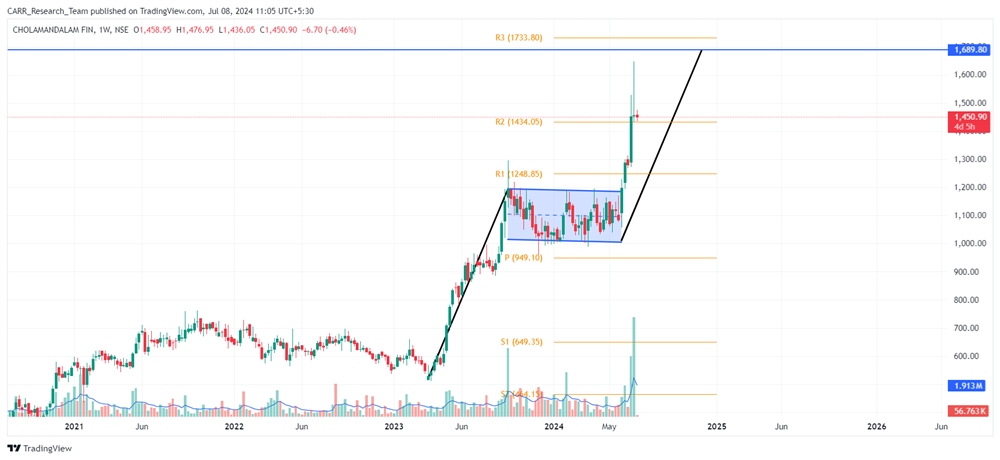
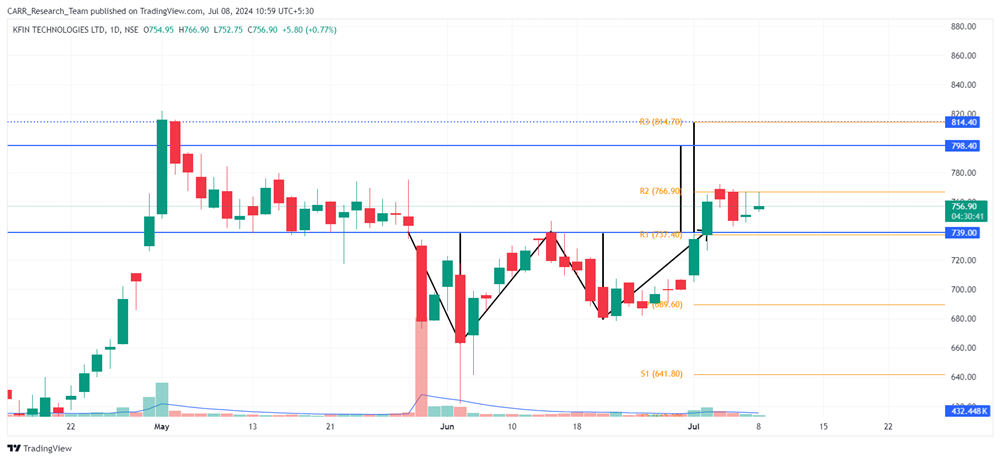
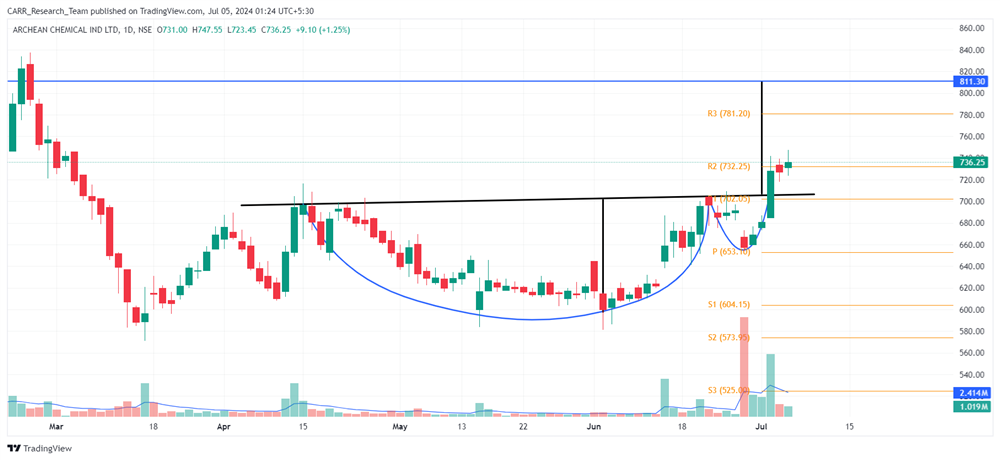
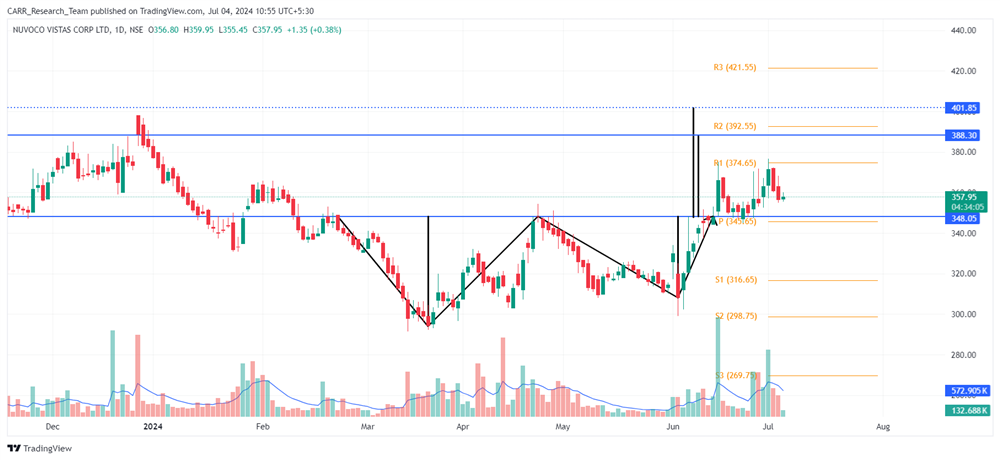
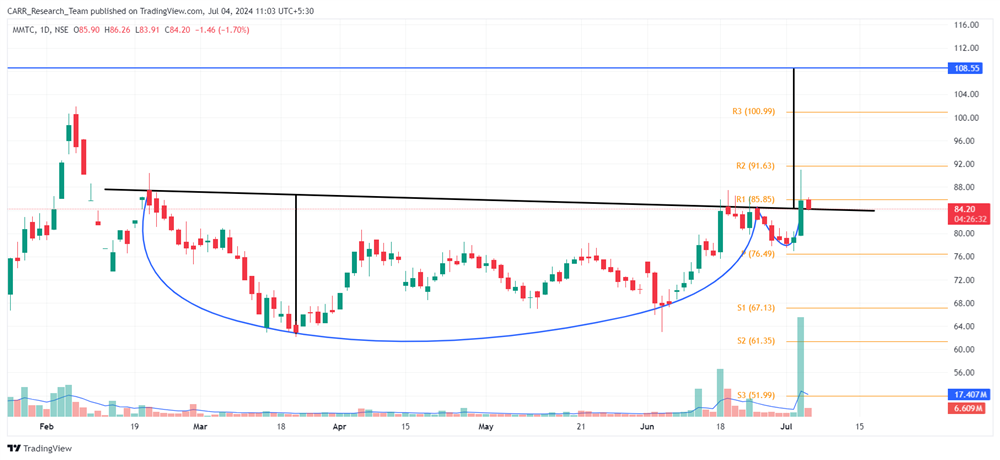
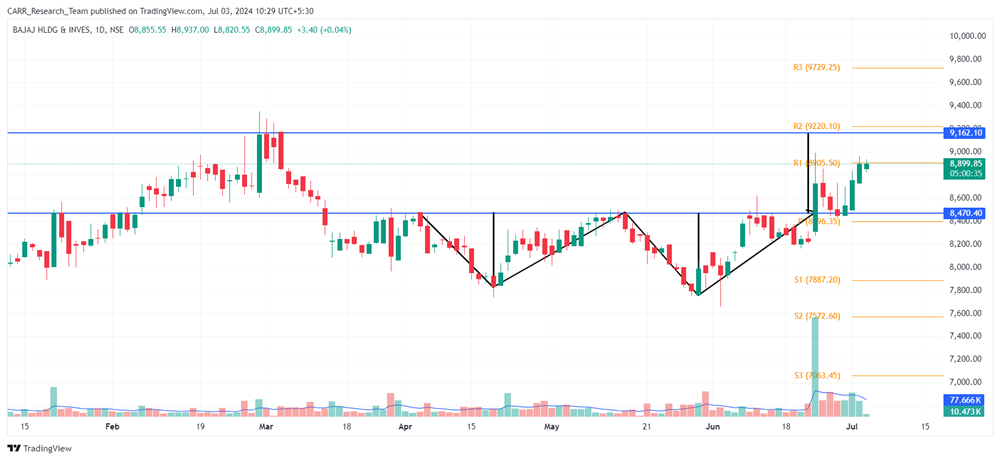
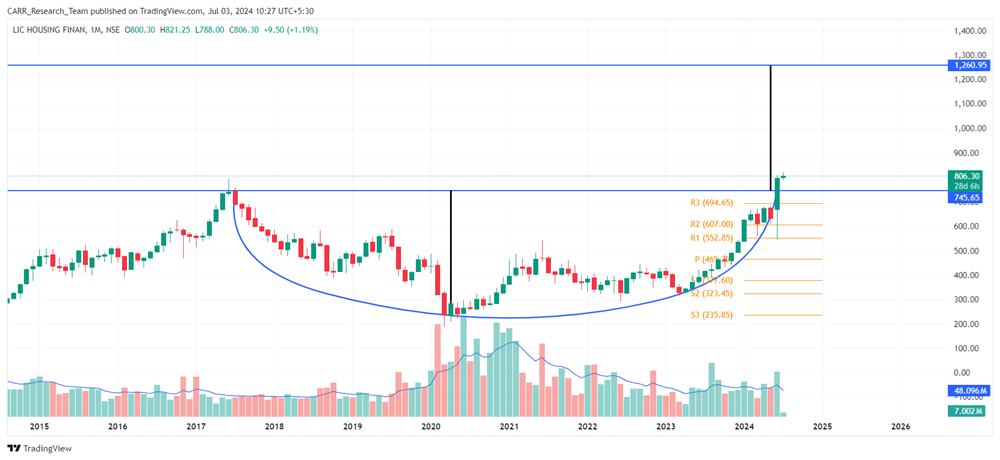
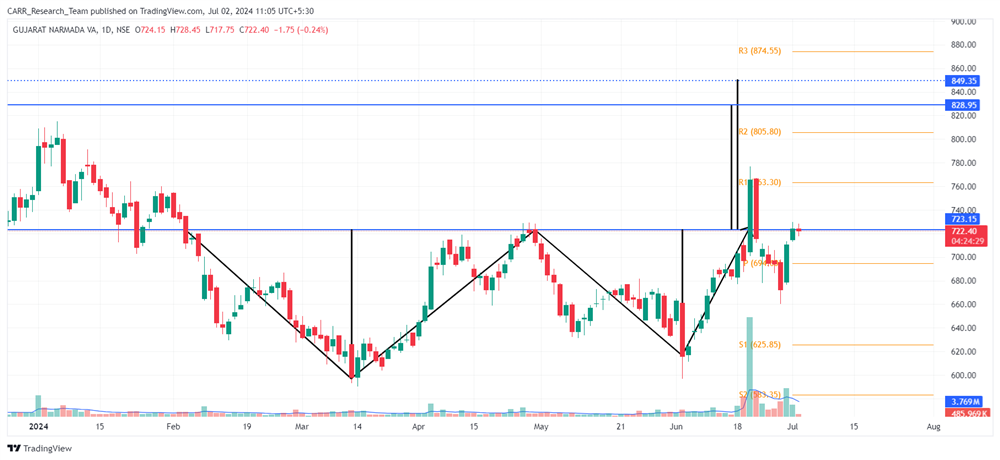
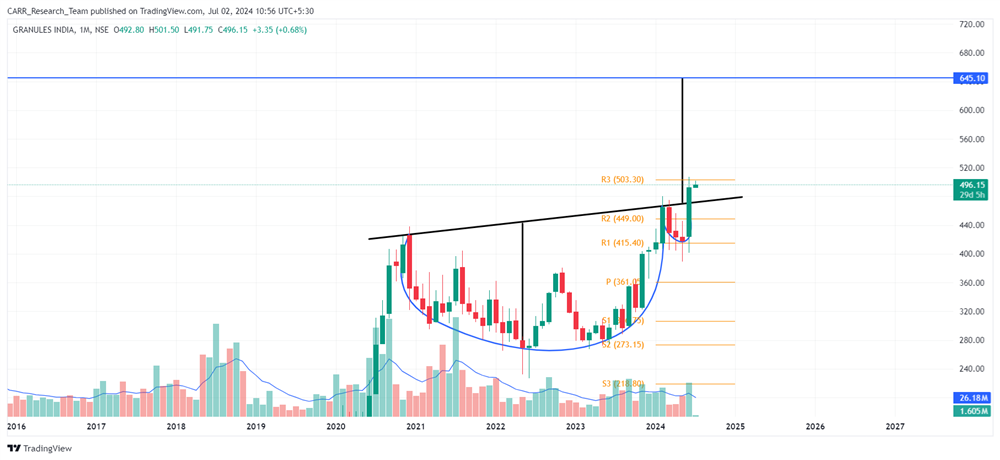
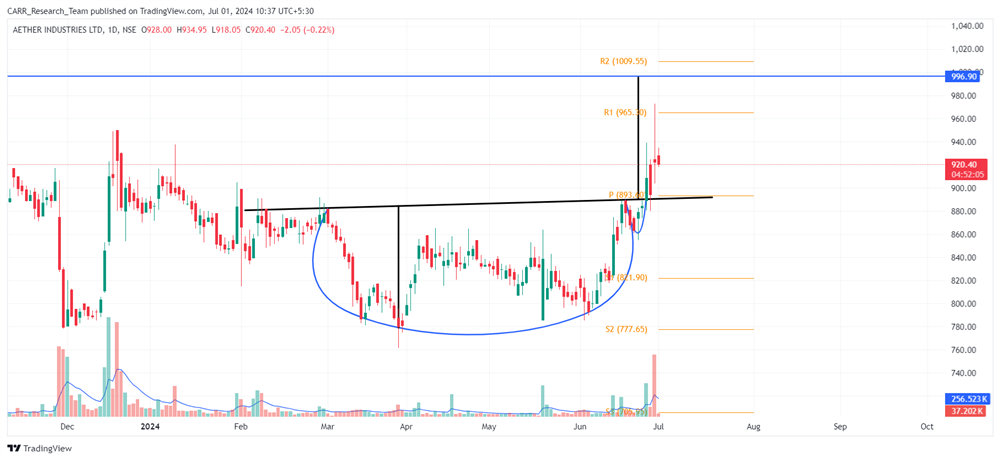
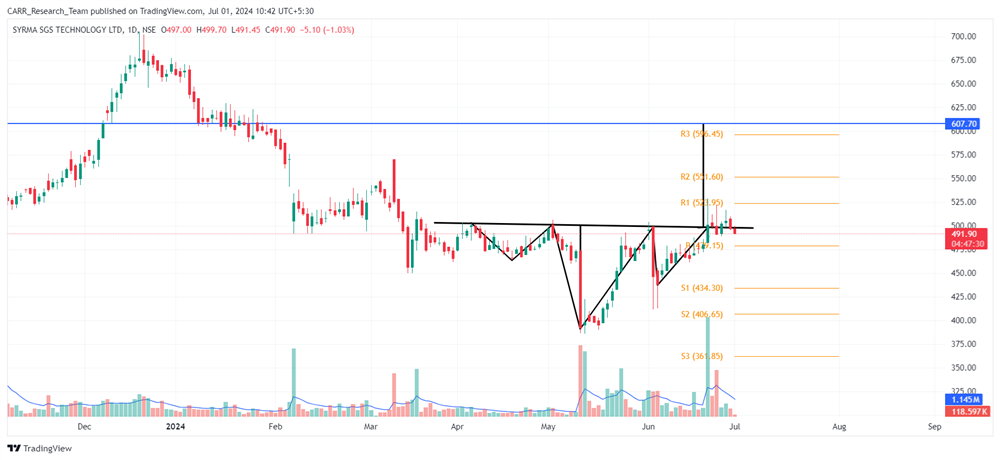
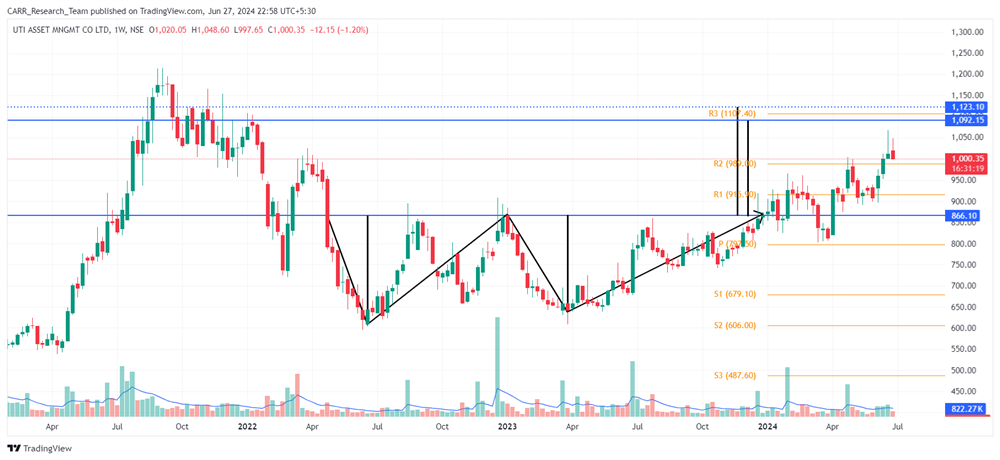
Stock name: Alkyl Amines Chemicals Ltd.
Pattern: Double bottom pattern
Time frame: Daily
Observation:
The stock has been declining since July 2021. From March to July 2024, it formed a double bottom pattern on its daily chart but failed to break out. The previous high of the pattern is acting as a resistance line, causing a downward movement after reaching it. The stock's RSI levels remain favourable. According to technical analysis, a breakout with strong momentum might lead to further upward movement.
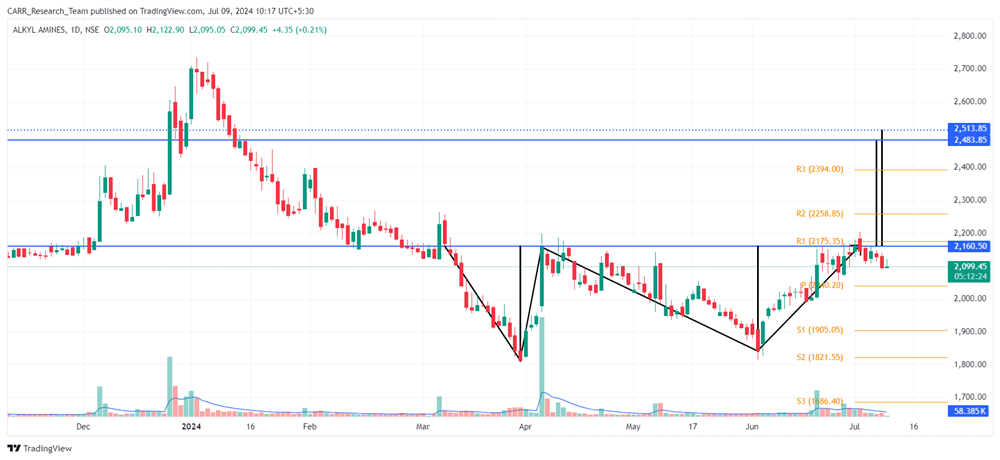
You may add this to your watch list to understand further price action.
Disclaimer: This analysis is purely for educational purpose and does not contain any recommendation. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any financial decision.

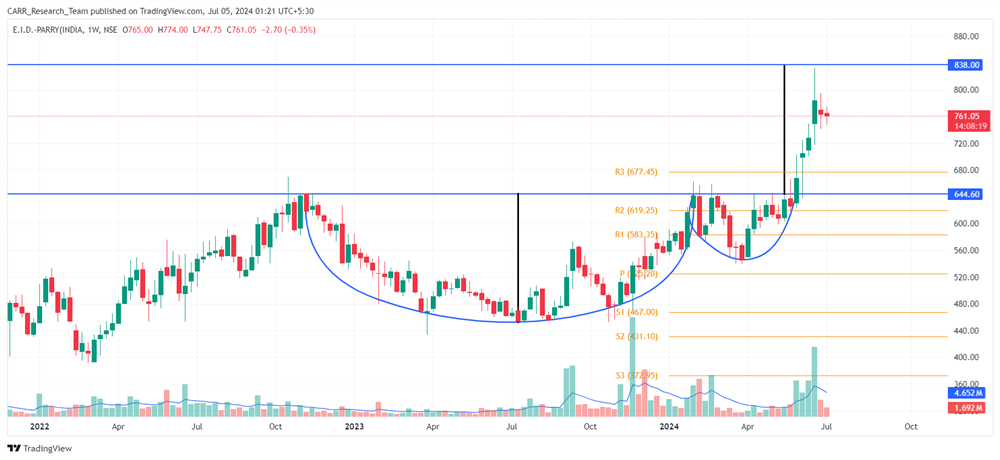
Stock name: Castrol India Ltd.
Pattern: Rounding bottom pattern
Time frame: Monthly
Observation:
Since December 2014, the stock has been declining, but it recovered in 2023 and is now back to its 2014 levels, forming a rounding bottom pattern on the monthly chart. Currently, the stock is still below the 2014 levels and hasn't broken out from the pattern, making this a potential resistance level. The stock's RSI is very high, suggesting possible consolidation or correction. Technical analysis indicates that a breakout with strong momentum might lead to further upward movement.
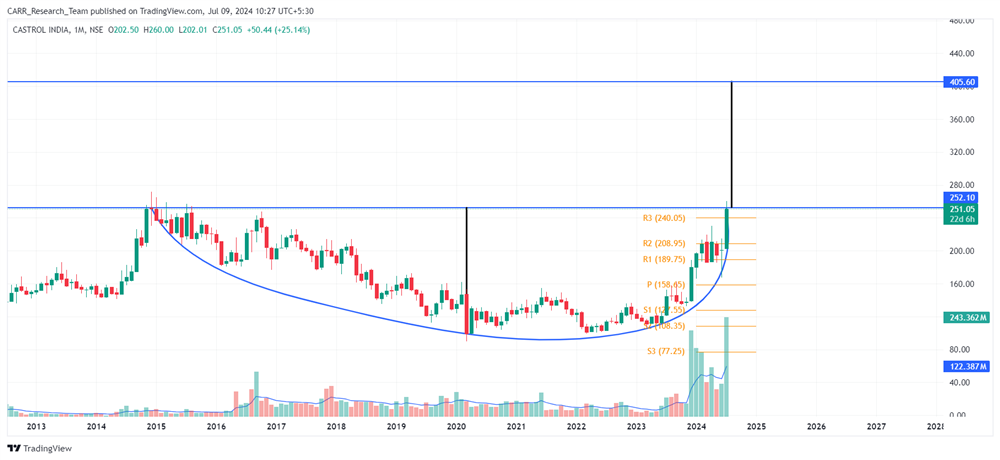
You may add this to your watch list to understand further price action.
Disclaimer: This analysis is purely for educational purpose and does not contain any recommendation. Please consult your financial advisor before taking any financial decision.
News for the day:
- Inox Wind has secured a 200 MW wind energy project order from a renewable C&I power producer, to be implemented in Gujarat and Rajasthan. The project will feature Inox Wind's latest 3 MW Wind Turbine Generators and involve turnkey execution along with multi-year operations and maintenance services. CEO Kailash Tarachandani expressed confidence in significant growth for FY25 and beyond.
- The Uttar Pradesh government has waived the registration tax on strong hybrid cars, benefiting manufacturers like Maruti Suzuki, Toyota, and Honda. Customers can save up to Rs 3.5 lakh on models such as the Maruti Grand Vitara, Toyota Hyryder, Innova Hycross, and Honda City hybrid. This policy, implemented through a July circular, aims to promote green vehicles. The state had already announced a three-year tax exemption for EVs last year, with a five-year benefit for in-state manufactured EVs. Despite the waiver, the low sales of hybrid vehicles mean the impact on the state exchequer will be minimal.
- Larsen & Toubro (L&T) announced the acquisition of Bengaluru-based SiliConch Systems for Rs 183 crore to strengthen its fabless semiconductor business. L&T Semiconductor Technologies Ltd. will finalize the deal by September, pending customary conditions. The acquisition includes an upfront payment of Rs 133 crore and a deferred Rs 50 crore over four years, contingent on meeting certain targets. SiliConch, established in 2016, specializes in semiconductor IP and IC design, with 30 granted patents and primarily serves OEMs and fabless IC companies in the US.